Our News
Attracting Leads Through Your Website in 2025 with Digital Marketing
How Can Businesses Turn Their Website into A Lead-Generating Beast with Digital Marketing? The competition for search visibility is heating up in 2025 ...
28th May, 2025
Learning and communicating patience in SEO is a good practice to start with. Hours of research can be directed into a well-written and insightful article, or similar efforts towards expertly optimising a key landing page. However, it’s potentially months until you see any reward.
SEO being labelled a long-term strategy is a fair safety net for digital marketing teams when proposing campaigns. To embrace the cliche of SEO, results really do depend on a number of factors surrounding the website, the project, business targets and the general industry.
But in most cases, there are some techniques to bring in results faster than you’d be comfortable promising to a client. Here’s my top six.
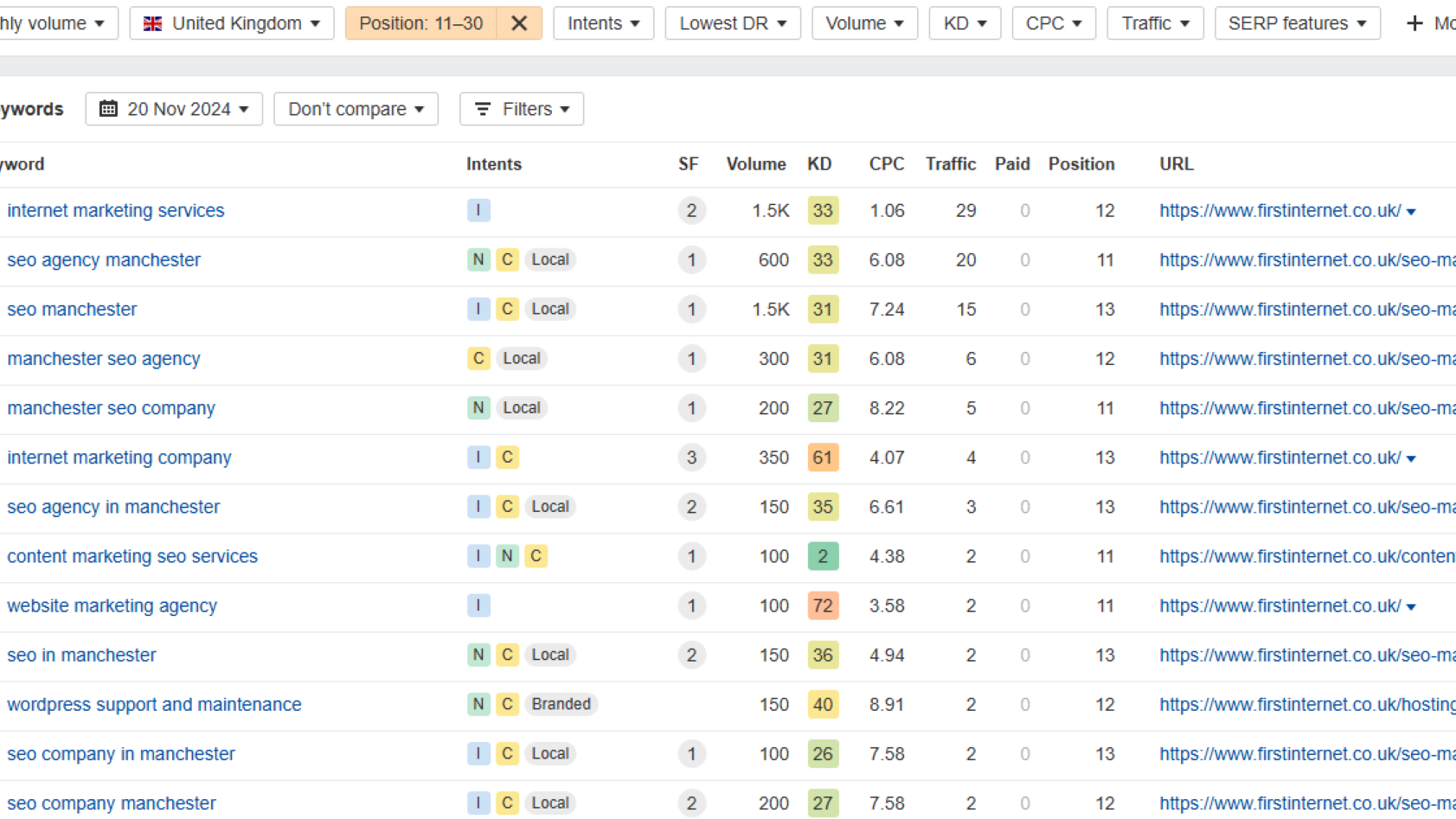
Despite a few quirks, Google Search Console is the go-to for search insights. This is giving us real user data, rather than guesstimates from other tools, and there’s plenty of information available that can be put into action for quicker results.
The best process I find myself utilising under the GSC umbrella is an activity that maps query data to target pages. By focusing on a single target page, the query data shows us how people have seen the result, or clicked on it. We can then start to make the decision of whether one) this is the right intent and two) what are we missing?
A good piece of keyword research should provide us data that hopefully aligns with what we’re seeing in query data. If not, we can investigate whether we’ve captured the wrong audience, or if there are some gaps in our research to fill.
I like this as a fairly straightforward but effective exercise in really understanding your clients’ audience and presence. It’s also useful in pointing your strategy in the right direction based on real data.
The start of any SEO project should involve a comprehensive onboarding phase, which helps align your clients’ goals with the strategy to be implemented. A big part of this will be the keyword targets that will make an impact. At this point, we can look at existing rankings that tend to show up on pages two or three, as it’s likely that with some focus we can improve this quite quickly.
However, the key here is choosing keywords based on their value, and not just because it might be easy to rank. There’s no use in spending a month of campaign resources on improving visibility for terms that don’t convert.
When executed against the overall SEO goal, this exercise is particularly satisfying (for us too) and offers the potential to deliver results much faster. It’s something we’ve successfully delivered time and time again, but the key to these results converting for clients lies within the nuances of why a particular keyword was targeted.
There will always be the argument of vanity metrics around generalising X amount of keywords to page one, but if they aren’t converting or sending better user engagement signals, it’s not really worth too much.
There’s a consistent push from Google on helpful content which more recently, is framed around both original and useful user experiences, but also an effort to combat and punish AI generated spam sites. What Google says and what actually happens are commonly debated amongst SEO professionals, but honest and creative agencies should be less affected. This is simply because principles of helpful content will be a strong thread that has been running through their strategies for years.
Delivering improvements on service pages is often somewhere you can have the most effect on lead generation. Key services pages should be all about building trust, answering questions and providing a direct touchpoint for contact. It can also be the toughest area to optimise, because this is where competition is strongest.
Everything could look right on the surface, there may even be good results for the service you’re pushing, but breaking through to increase share of voice and up those conversions just isn’t happening. If you’ve checked off the usual suspects then it’s probably time to revisit a fundamental step of working out how well your page answers the question.
Are your competitors providing better or more original ideas? Does the business itself need to diversify the offering? Ensuring these content gaps are filled can sometimes be all the algorithm is looking for to help bump up your presence for those key topics.
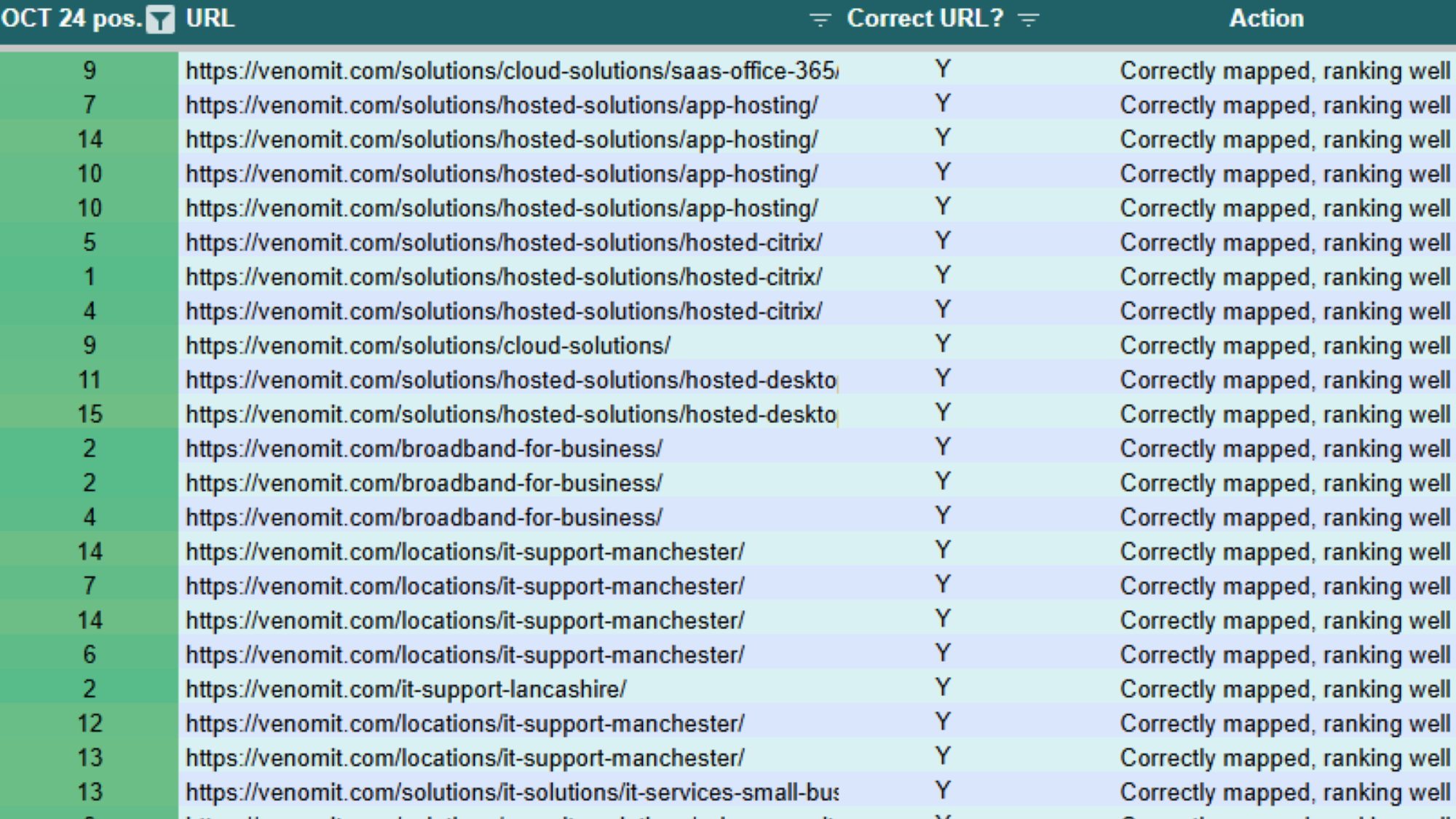
Another activity that builds on query mapping is how and when to look at optimising for CTR. For one client, search impressions were flying out the wazoo, and for the right search terms. However, the clicks didn’t reflect the jump in visibility, which naturally took us to CTR exercise.
Using CTR % metrics, alongside URL and query data mapped correctly, it’s possible to build a system of on-page optimisation to tighten everything up and target the queries with the best impressions.
We built a tool using VBA code, with the idea of matching underperforming URLs against the relevant search queries,returning a list of related keywords to focus on. Watch this space for how this develops.
Even without the benefit of some automation, the end result should provide a useful data set of key URLs that can be improved for the searches people are finding them with. Making informed changes such as these is going to start having an effect within a few days, rather than months down the line.
It’s tempting to try and cover all possible bases with dedicated landing pages, but when this becomes too granular you end up with saturation. Pages can become too similar when they try and target different semantics of the same search intent, which means Google has a problem deciding which page to pass the authority to.
For all our SEO projects, we keep a comprehensive tracked list of keywords that end up grouped into categories.
By looking at a variation of keywords within one of these categories, and analysing which pages are being ranked, we can quickly see how well the topic has been targeted.
If you find there are different URLs being ranked within a single category, you’ve probably got a case of cannibalisation to look at. This can be quite quickly addressed with some fundamental SEO practices to help direct search engines, and ultimately your target audience to the page they are looking for.
If it makes sense to the business and services they offer, a local presence in search is an absolute must have.
The first thing you’ll want to see quite quickly from implementing a localised strategy is the jump in impressions. This means you’ve built the foundations correctly and search engines have started showing your pages for local searches. It’s then down to the wider project strategy to further build on this visibility.
Localised landing pages help build trust, and offer customers a more ‘direct’ route to getting in touch – whether it’s local numbers, map entries or a contact form.
Plugins like Page Generator Pro are easily manageable ways to use templated landing pages, with enough variation to target your desired areas.
If you get to this stage it’s probably more difficult not to see some results.
Ultimately, SEO results don’t need to be gatekept with months of buffering while you wait for something to happen. A well maintained website with an ongoing and well-directed SEO campaign puts you in a position to try new things, focus on new targets and expand visibility, with a realistic expectation of seeing an impact. Our client, Black Brick Property, was in exactly this position, looking to expand from London to Country. Within two weeks of publishing new pages, we were on page one, with position one following shortly.
It’s wise to be realistic about the likelihood of ROI on SEO projects, managing expectations for both clients and your team. This doesn’t mean there aren’t ways to achieve something tangible in a shorter time frame.If you’re looking for a full-service agency to help build your brand online, get in touch with us today and we’ll get you started.
Our News
20th November, 2024
Call us on: +44 (0) 161 941 5330 or email us: info@firstinternet.co.uk
Get in touch today!